| BBA4103: Introductory Business Statistics |
Question 1
Consider the result of a test on the subject of Statistics final exam taken by 120 students, as given in the following relative frequency distribution:
Grade Less than 50 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-100 Cummulative Frequency 15% 10% 30% 25% 15% 5%
How many students received at least a 70 on this exam?
Question 2
According to the empirical rule, approximately what percentage of normally distributed data lies within one standard deviation of the mean?
Question 3
The following is a sample of ages (in months) of 18 children at a daycare:
36 42 18 32 22 22 25 29 30 31 19 24 35 29 26 36 24 28
You are required to provide the following:
- The mean age of the children
- The median age of the children
- The inter-quartile range of the children age
- The standard deviation of the children age
The following formula is used to calculate the Pearson Correlation Coefficient
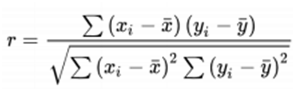
r.
The following table lists the number of days that five houses had been put up for sale, as well as their selling price.
X (days) 45 12 3 17 32
Y ($’000) 275 401 420 212 365
You are required to calculate the correlation coefficient r between the number of days (X) and the selling price (Y) for this sample.
Question 5
The following data lists eight different investment amounts (X) and the amount of interest they earned (Y):
X $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 $10,000 $500 $5,000
Y $50 $100 $150 $500 $25 $250
How would you describe the relationship between investment amount (X) and interest earned (Y)?
c) r will be exactly one
Question 6
A random sample of 10 items is taken from a normal population. The sample had a mean of 82 and a standard deviation is 26. Which is the appropriate 99% confidence interval for the population mean?
You are required to express the above information in a statistical equation.
Note: It is a small sample, so the t-value should be used instead of Z-score.
Question 7
Classify each one of the following variables as either measurable (continuous) or categorical. If a variable is categorical, further classify it as either nominal or ordinal. Justify your answer. (Note that no marks will be awarded without a justification.)
- Delay times of a particular train.
- The type of fruit juice, based on the kind of fruit, produced by a company. iii. The difficulty level of a ski slope.
- The quantity of wine produced by a vineyard.
Question 8
An insurance salesman visits one of two areas each day; namely A and B. The choice of which area to visit is made randomly every day with area A being chosen 40% of the time, whereas area B is being chosen with a probability of 60%. When the salesman visits area A there is a 40% chance that he will make an insurance sale, and when he visits area B the chance of a sale is 30%.
What is the probability that the salesman will make a sale on a typical day? ii. Suppose that a sale was made on a particular day. What is the probability that the salesman visited area B?
Question 9
State whether the following are true or false and give a brief explanation. (Note that no marks will be awarded for a simple true/false answer.)
- A correlation coefficient of 0.9 between variables A and B suggests that there is a positive influence of variable A on variable B.
- The lower the constant in the regression equation, the weaker the correlation.
- Consider a confidence interval for a population mean, obtained by a sample, and assume that the population variance is unknown. If we add 5 to every number in the sample while keeping everything else the same, the width of the interval will not change.
- When testing a hypothesis, we use a one-tailed test if we want to test whether the parameter is different from what is stated in the null hypothesis.
- A population list is needed in order to conduct stratified random sampling. vi. In some cases, the median can be larger than the upper quartile.
Question 10
The following data show the marks (in %) achieved by a random sample of students in an end-of-year examination:
62 78 88 63 50
66 90 93 33 35
41 48 66 63 96
82 92 62 47 37
99 95 47 61 60
36 80 70 58 73
- Carefully construct a stem-and-leaf diagram of these data.
- Find the median and the interquartile range.
- Comment on the data given the shape of the stem-and-leaf diagram without any further calculations.
- Name two other types of graphical displays that would be suitable to represent the data.